Understanding Benign Soft Tissue Tumors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction:
Benign soft tissue tumors are non-cancerous growths that develop in the various tissues of the body. Despite the term “tumor,” it’s important to note that these growths are generally harmless. In this article, we will provide valuable insights into benign soft tissue tumors, including their types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, to help you understand them better.
What are Benign Soft Tissue Tumors?
Benign soft tissue tumors encompass abnormal growths that occur in muscles, fat, blood vessels, tendons, nerves, and other connective tissues. Unlike their malignant counterparts, benign tumors do not invade nearby tissues or spread to other body parts. They typically grow slowly and remain confined to the site of origin.
Types of Benign Soft Tissue Tumors:
Several types of benign soft tissue tumors exist, each originating from different tissue types. Here are some common examples:
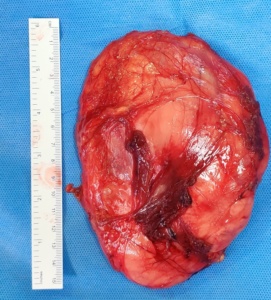
- Lipomas: Lipomas are the most prevalent benign soft tissue tumors, arising from fat cells. They often manifest as soft, movable lumps beneath the skin. While lipomas are usually painless and rarely require treatment, they may be removed if they cause discomfort or affect appearance.
- Fibromas: Fibromas develop in fibrous tissues like tendons and ligaments. These tumors can lead to localized swelling, palpable lumps, and may cause discomfort or restricted movement.
- Hemangiomas: Hemangiomas are non-cancerous growths formed from blood vessels. They can occur on the skin or internally. Superficial hemangiomas appear as red or purple birthmarks, while deeper ones may not be visible but can cause complications if they affect vital organs.
- Schwannomas: Schwannomas originate from Schwann cells, which protect nerve fibers. These slow-growing tumors can appear in various body parts, causing symptoms like pain, numbness, or weakness.
Other rare types of soft tissue tumors are as follows
- Benign fibrous histiocytoma (Spindle cells)
- Fibromatosis (Desmoid Tumour)
- Neurofibroma (Neural)
- Neurilemmona (Neural)
- Giant cell tumours of tendon sheath (Spindle cells & Synovium)
- Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis (Synovium)
- Myxoma (Myxoid)
- Leiomyoma
- Glomus Tumour (Blood Vessel)
- Rhabdomyoma
Causes and Risk Factors:
The precise causes of benign soft tissue tumors remain unknown. However, certain factors may increase the risk, such as genetic predisposition, previous radiation exposure, or underlying syndromes.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
- Symptoms of benign soft tissue tumors depend on their location and size. Common indications include painless lumps, swelling, limited mobility, discomfort, or cosmetic concerns. If you notice any abnormal growth or persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
- To diagnose benign soft tissue tumors, doctors conduct physical examinations and may order imaging tests like ultrasounds, MRIs, or CT scans. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to analyze a tissue sample further.
- https://bonecancer.in/2020/05/01/arriving-at-diagnosis-services/
Treatment Options:
Treatment for benign soft tissue tumors depends on factors like type, size, location, and symptoms. In many cases, no treatment is required, especially if the tumor is small, asymptomatic, and non-threatening. However, if the tumor causes discomfort, functional impairment, or cosmetic issues, treatment options may include:
- Observation: Regular monitoring of the tumor’s size and progression through imaging tests may be recommended.
- Surgical Removal: Surgical excision is often preferred for symptomatic, rapidly growing, or problematic tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor while preserving surrounding healthy tissues.
- Other Interventions: Alternative approaches such as cryotherapy (freezing the tumor), laser therapy, or medication may be considered in specific cases.
Conclusion:
- Benign soft tissue tumors, though non-cancerous, can still have an impact on your health and well-being. Understanding their types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial.
- If you suspect the presence of a benign soft tissue tumor, consult amedical professional who can provide accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate management plan tailored to your needs.
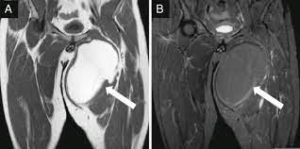
Lipoma Soft tissue tumourImage of lipoma of thigh sourced from https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Lipoma-with-MR-imaging-features-of-lipoma-a-Coronal-T1W-and-b-STIR-MR-images-showing-a_fig2_230871147