Reaching a Diagnosis
**Arriving at a Diagnosis**
*Understanding Symptoms, Indicators, and Therapeutic Alternatives for Sarcoma*
**Diagnostic Imaging Techniques**
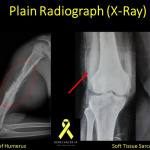
**X-ray Imaging (Plain Radiographs)**
Plain radiographs represent the initial imaging examinations performed when a patient presents with a suspected condition.
These tests are straightforward, swift, and involve lower radiation exposure in comparison to computed tomography.
Plain radiographs provide detailed insights into the tumor’s characteristics, stage, progression, its impact on the surrounding bone or soft tissue, the body’s response to the tumor, and aid in determining the appropriate surgical approach.
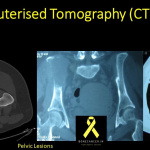
**Computed Tomography (CT)**
CT scans offer an improved view of bone structure, cortical continuity, cancellous bone integrity, and periosteal reactions.
While more expensive than plain radiographs and entailing greater radiation exposure, CT scans offer superior detail.
CT scans are particularly advantageous for axial imaging.
They are employed for staging, especially in the chest area to identify metastasis (HRCT).
**Ultrasound (USG)**
Ultrasound can assist in distinguishing solid components from cystic ones, aiding in characterizing soft tissue tumors.
It serves as a valuable guidance tool for biopsies of soft tissue tumors, facilitating precise targeting of the solid tumor site for pathological diagnosis.
Ultrasound is also used as a supplementary tool in diagnosing bone and soft tissue tumors.
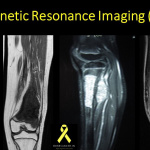
**Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)**
MRI stands as the most comprehensive and informative imaging technique for assessing the local stage of bone tumors.
It offers several advantages, including the absence of ionizing radiation, superior contrast, multi-planar visualization, and improved tissue definition.
The soft tissue contrast provided by MRI is especially valuable, enabling differentiation between neighboring structures.
The use of gadolinium contrast or enhanced (diffusion-weighted) MRI can further assist in refining the diagnosis.
MRI can detect certain lesions within the same limb, referred to as “skip lesions” or satellite lesions.
Additionally, it aids in measuring the tumor’s extent and supports the reconstruction process.
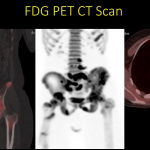
**PET-CT Scan**
Bone and soft tissue sarcomas can spread regionally and distantly, a phenomenon known as “metastasis.”
The most common site of metastasis is the lungs, followed by bones and other organs.
Staging involves evaluating the extent of sarcoma’s spread to other areas of the body, and PET-CT scans play a critical role in this assessment.
The most frequently performed PET-CT scans include 18-FDG (fluorodeoxyglucose) PET-CT, followed by 18-NaF (sodium fluoride) PET-CT, primarily for staging purposes.

9 Comments